Cloud Computing And The Environment
Cloud computing is a way of managing IT resources from a remote location as per the Pay as you Go model. It allows on-demand delivery of computing power, database, storage, applications, and other IT resources via cloud service platforms (for example AWS, Azure, Alibaba Cloud, Google Cloud, etc.) via the internet.
What is cloud computing exactly? In simple words, it’s one way of delivering IT services over the internet. For example, you buy web hosting, but that web hosting is not on your premises. You access and manage your hosting services via the internet. Similar is the cloud. But it can do many more things rather than just web-hosting.
With various tools and services provided, it has helped many organizations to focus on their business strategies. Organizations need not worry about the organizing and maintenance of IT Resources. It gives the organization more time to focus on its business strategies.
The concept of cloud computing has existed for the past 4 decades. In this article we will learn about what is cloud computing, how it deliver services, what services are there etc. It is very important to understand the IT infrastructure before we understand the concept of cloud computing.
Life before Cloud Computing – Traditional IT Infrastructure

In early days, organizations used to maintain their in-house data centers. Data centers are like a centralized location where all the IT resources are located. When I say IT Resources, I mean the equipment like server, switches and other networking equipment, power supply, storage, etc.
They all are kept together and configured altogether to work as a Data Center. Information is shared between the data center and computers within the organization as per the user access levels. These data centers can be for fulfilling the requests within or outside the organization.
For example for testing and development the computers within the organization can connect with the data center. And for web presence of the organization a web server is installed on the same data center which can be used. Now the organization want’s to go online to expand it’s business. They can simply add one more server in the data center and host all the related web applications and make it public facing. So, the data center can be used to fulfill both organizational and public interactions over the web at the same time.
In-house data centers are costly but very secure and reliable. It is fully controlled and managed by the organization. Hence, the organization has to bear the cost involved in the updates and upgrades of the software and hardware.
Example
Let’s say that an organization has to open it’s own data center there is a huge upfront cost involved. Consider the below points:
- The organization will need a location to set up the data center.
- Then the organization had to buy all the IT resources.
- An IT Technician had to be assigned who will be responsible for assemble, configure and manage all the IT resources
- Other recurring charges like upgrade of the hardware and software.
- To ensure the servers are up all the time, there has to be a dedicated power supply and dedicated broadband connection.
- Because there will be so many machines, so it will generate great amount of heat. Therefore proper cooling facility to control the IT resources from over heating.
- Proper security controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can enter the server rooms.
- Proper housekeeping staff to ensure the cleanliness of the data center.
There are many other related things which contribute in the costing of the data center. For a small organization it’s not feasible to build their own data centers. Therefore they mostly prefer to buy a hosting from a hosting provider or get in touch with a cloud vendor and launch their servers online.
However the in-house data centers are very secure, flexible , scale-able and the organizations have full control over it. Usually the in-house data centers are managed by big organizations like Microsoft, IBM, Google, Facebook etc or by organizations with extreme business critical needs.
KEY TAKE AWAY
What is a Data Center?
What are the components involved for building a Data Center.
Cost involved in setting up a small Data Center.
What organizations can build their data center.
PROS and CONS of an in-house Data Center
Cloud Computing: Overview on Cloud Managed Infrastructure
Cloud Computing definition in simple words is the delivery of variety of IT services over the internet. These services could be anything from creating the server server, network, storage to applications, analytics, databases and much more. You can think of cloud computing as a data center which is located at a remote location. You do not have to worry about the purchase and maintenance of IT resources.
In cloud computing organizations have independence of choosing each configuration of the IT resources. For example, you need a server for your web application. You can choose the configuration of the server precisely like RAM size, Hard disk size, CPU cores, OS etc. Once you have chosen the configuration, you can launch the server with the click of button. The server will be up and running in a few seconds.Once the server is launched you can choose how the server should communicate within and outside the organization.
Cloud computing services have their own benefits when it comes to billing plans. In cloud computing you are not buying the IT resources, you are utilizing the IT resources on rent instead. As per the different billing plans you will be changed like pay as you go, on demand, discounted plans etc. You can use the services and pay for the time you have utilized the IT resources.
Once your cloud servers are up and running, there are various monitoring services provided to track down the performance and health of the IT resources. Also, in case of heavy traffic on the server or if the servers are highly utilized then additional servers can be easily made available on real-time to balance the load.
Example
Spike of users on your web server can impact your server’s performance. For such cases there is a concept auto-scaling and load balancing. Once configured, it will automatically scale up the additional servers when there is spike. Once spike is reduced, it will automatically scale the servers down. In such cases, you will only be charged for the time the additional servers were utilized.
Cloud computing offers many readily available services as per the need of the organization. This results in saving ample amount of which the organization can utilize in focusing on their business strategies. Because IT resources are not owned by the organization therefore it results in cost effectiveness. Organization can control the configuration of the IT resources efficiently at any given time. The only thing they need is a computer or a multi-media cellphone with internet connection.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
- When needed, IT resource are readily available for configuration and use.
- Cost effective.
- High Performance and speed
- Data Security
- With data replication on multiple data centers, back-up is available as and when required.
- Ability to scale up services as per the requirement on real-time.
- Wide range of IT resources available at a click of a button.
Overview on Cloud Geographical Distribution
Although you won’t be managing the physical data centers but it’s good to have an idea about how these data centers are distributed over the globe. Cloud service provider will give you independence of choosing the location of your data center. These locations are divided into sub locations known as Regions, Availability Zones and Local Zones etc.
Let’s say you are working in Delhi and there is a data center located in Mumbai. You can opt for Mumbai data center. Because the data center is near data will be accessible more faster than any other location outside the country. Understanding the concept of Regions and Availability Zones will help you to differentiate between locations.
Regions: Regions are independent locations distributed across the world. Regions are the geographical locations where you can choose to host your IT infrastructure. (Example: US East or US West). Each region is isolated.
Availability Zones: Availability zones are the locations of the data centers. Minimum of 2 availability zones are there in every Region. For example, US East Region has 2 Availability Zones in Ohio (us-east-2) and Northern Virginia (us-east-1).
If you are in US and want to host your server on cloud you can choose Region and availability zone and launch your server.
Cloud computing provides various deployment and service models. The deployment model specifies where the infra is located, who can access and control it. Cloud computing service model describes what part of cloud services you can utilize. Let’s try to identify and learn more about these service and deployment models.
Cloud Computing Deployment Model
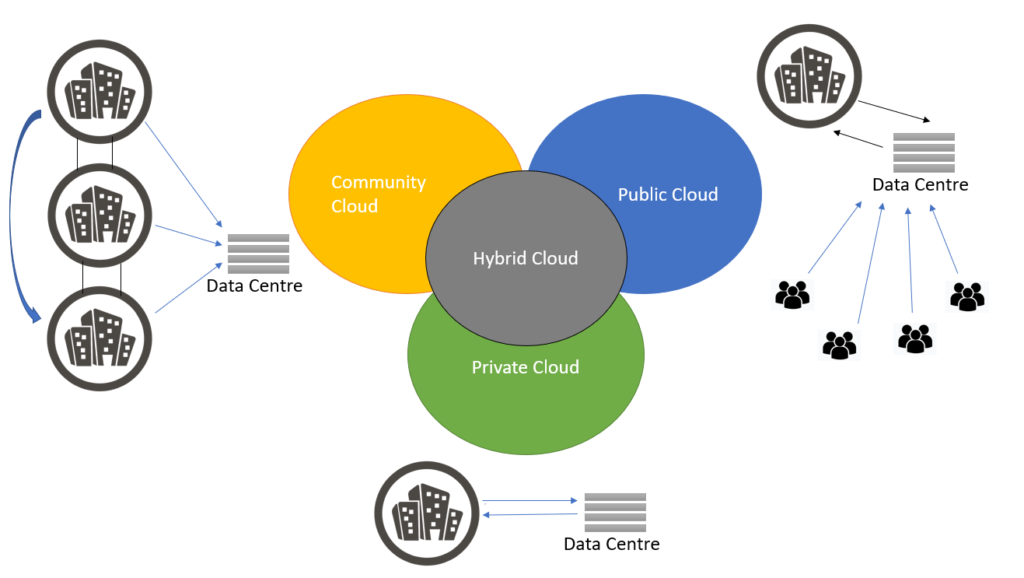
Deployment models in cloud computing refer to the location where the cloud infrastructure is located. Also in addition to this, it also defines the control of the particular deployment models. Deployment models are like the location where the organization wants the infrastructure to reside. Each deployment model has a specific configuration of the environmental framework. On the basis of these configurations, there are few available deployment models. These are:
- Private Cloud
- Public Cloud
- Community Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
These deployment models provide an effective and efficient ecosystem of IT services on which businesses run. Various enterprises have opted for these deployment models as per their business goals to manage their IT needs. So let’s go ahead and learn more about these deployment models.
Private Cloud
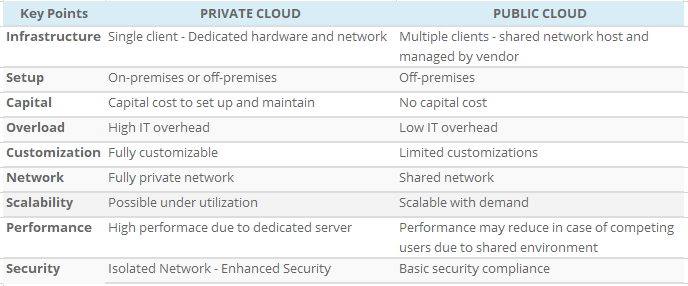
A private cloud is a cloud deployment model managed by/for an individual organization. The IT resources within the private cloud are inter-connected with a private network. This deployment model is opted by enterprises that want to safeguard their mission-critical operations, security, share the internal workloads, and their changing business requirements.
As the name suggests, private clouds will not be accessed by external links. Only a few people within the organization will be provided limited scope access to the private cloud. There are various cloud vendors available in the market which are providing private cloud deployment models. A private cloud can be hosted in-house or on a remote location as per the need.
The private cloud deployment model is the most secure deployment. As it can be accessed only over a private network, there is less risk of security breaches. The organization will be responsible for the maintenance of the infrastructure.
Private cloud deployments are best for large organizations with high IT budgets. Organizations that need cloud benefits but want to safeguard resources at the same time can opt for private cloud deployment. Private can be used to manage web backends, databases, virtual private infrastructures, etc.
PROS:
- Many possible customization options.
- Due to the isolated network, the private cloud is highly secure.
- Greater control and reliability on the infrastructure including the geographical location.
CONS:
- Operating expense in maintenance and training.
- In the case of on-premise set-up, it becomes less scalable and redundant.
Public Cloud
Unlike Private Cloud, the Public Cloud deployment model is available to the general public over the network. Public cloud is opted by enterprises that have fewer privacy concerns. Public cloud is more popular among businesses running their websites, webmails, cloud storage, etc. So you can understand that if you are able to see this website, it is available on the public cloud.
The resources and location of public cloud deployment are managed by cloud vendors. This means there will be no cost involved in setting-up and maintenance of the infrastructure. It works on the shared hosting environment. Enterprises that have opted for a public cloud deployment model need not worry about the IT Infrastructure. This allows them the independence to focus on their business strategies more efficiently.
In terms of cost and maintenance, the public cloud deployment model is most appealing amongst all the other deployment models. Best suited for organizations with variable business demands. Ease of launching the IT resources within a few clicks and flexible pricing models make it more attractive.
PROS:
- Reduced time for launching IT resources
- Cost-effectiveness as the enterprise needs not to set-up or maintain the environment.
- Effective pricing models like pay as you go wherein the company has to pay only for the time the services used.
- Location independence.
- Easy to manage.
CONS:
- High-Security risk.
- Performance issues based on usage.
- Less scope of personalization due to lack of control.
Community Cloud
A community could model somewhere lies between private and public clouds. Unlike a private cloud, in the Community Cloud deployment model, organizations with similar objectives collaborate together to share and exchange their IT-specific objectives. The difference is that the community cloud operates between similar organizations and is not open to the public.
The best example of a community cloud is banks where various transactions take place between different banks. A community cloud is the shared cloud deployment model that belongs to a particular community. Such models can be hosted internally and also can be managed by third-party vendors.
The community cloud deployment model is best suited for organizations that have similar cloud computing needs. Community cloud does not exist in every community therefore to acquire maximum benefits there have to be organizations with similar objectives.
PROS:
- Reduced cost as compared to the private cloud.
- More secure and reliable as it’s not open to the public.
- Collaboration and data sharing becomes easier between organizations.
- More scalable as compared to Private Cloud
CONS:
- Organizations will not be getting the full benefit of the private or public cloud.
- The cost is higher as compared to the public cloud deployment model.
- Does not exist in every community.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is the envelope of the best features of the other three cloud deployment models. Enterprises have the liberty to choose the features and host their IT Infrastructure as per their requirement.
For example, companies can host their critical business applications related information on a private cloud, website, and public-facing information on public cloud and resources and applications which need to collaborate within multiple organizations on community cloud.
Also, organizations can make use of private clouds for basic processing but can utilize public cloud resources in case of the spike. This process is also known as Cloud Bursting which can actually help in increasing the up-time and healthy performance.
PROS:
- Improved Security and Privacy.
- Highly scalability and flexibility.
- Reasonable price.
CONS:
- The model is complex as it is a mixture of multiple cloud deployments.
- High Maintenance.
- The initial cost involved in activating the infrastructure.
Cloud Computing Service Model
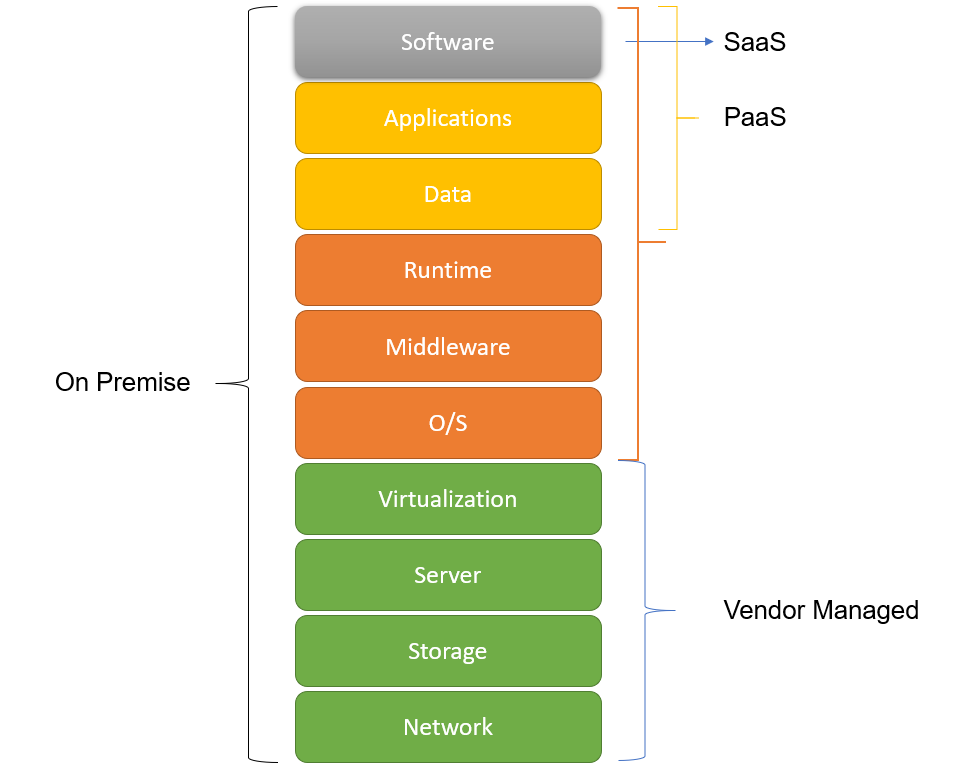
There is various service provided by cloud. Each of these service models has its own set of benefits that fulfills various business needs. It is important to understand what these service models are and what they offer. Understanding these service models will help to simplify the requirement and choose the right service model as per the business requirement.
Infrastructure As A Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a service or IaaS is the most flexible service model in which cloud vendors provide the liberty to access and manage the computing resources. Organizations can choose the computing capacity, storage, networking features, and set up their infrastructure in a few clicks.
Example
XYZ Corp has opted for the IaaS service model. In case the organization needs another server, it can choose the CPU, Memory, Disk Size, Location of the Data Centers, region and related networking details, and Launch the server. In a few seconds, the server will be up and ready to use. Similarly, in case there is any need for enhancing the firewall or VPN or adding additional disks or servers, etc can be easily achieved with this service model.
Within IaaS there are various services available related to Compute, Storage, Monitoring, Network, IAM, etc. Also, there are various monitoring features available to keep track of the health of the resources. Organizations can access and manage/monitor all the resources remotely over the internet.
The best part of IaaS is the pricing models, for example, the user only has to pay for the time the IT resources are utilized by him. These pricing models may vary from vendor to vendor.
Organizations with fluctuating IT requirements use the IaaS service. Like, high computing requirement during peak hours, ability to scale the computing capabilities in case of spikes without additional hassle. The organization has full control over the configuration of hardware infrastructure.
This service model is like choosing every configuration of your data center, but instead of buying it, the organization provisions the computing resources over the cloud. Popular examples are Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, etc.
Platform As A Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service or PaaS is a cloud service delivery model wherein a virtual runtime environment is provided for testing and developing the applications. PaaS service vendor provides and manages the hardware, storage, and networking allowing the organization to focus on development, deployment, and testing of the applications.
PaaS provides the runtime environment, application development tools, and deployment tools. The PaaS platform is accessible over the internet like other cloud services. Organizations can work broadly without extra knowledge of system administration. Developers only need a PC and a working internet connection.
Popular examples are AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine etc.
Software As A Service (SaaS)
Software as a service is used by the end-users. SaaS is also called as software on demand. Software as a service is a software distribution model in which an application is hosted with a cloud service provider and distributed over the internet. This service model makes the application available over the internet for use. Users can use the application which is already installed and running over the internet.
In the SaaS model, users will have their personalized log in details. They can access the application from anywhere anytime and start working on it. Users need not worry about the infrastructure or platform on which the application is running as it is all managed by the cloud service provider.
Users only have to pay the subscription of the SaaS based application and they can access the application as per their access levels. One of the best examples of SaaS is Gmail. You can create your credentials on Gmail and can start using it. Without worrying about the infrastructure and the platform, you can use the service like emails, appointments, calendar schedules, etc.
Apart from these 3 standard service models, there are many other service models that are finding their roots as a cloud service. Very soon we may see some more addition to these service models. Cloud computing is the new face of the IT industry. With technological advancements, there are many additions to various cloud delivery services and there are many more to come.

Conclusion
In this overview of Cloud Computing, we have discussed the standard model and standard service delivery model of cloud computing. But apart from IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, there are many more emerging delivery models that can bring massive changes in today’s IT market. Some of those examples are NaaS (Network as a Service), TaaS (Testing as a Service), IPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service), FaaS (Function as a Service). The benefit of the Cloud services lies in the type of service model chosen by the organization. It’s hard to mention that what are the companies which have adopted cloud computing methodology, but there are many big names that top the list.
Cloud computing is still at its early age of adaption even when it exists for more than a decade around us. The pricing models between different vendors vary from vendor to vendor. Moving to cloud computing, organizations will have more time to dedicate to critical business development rather than worrying about their IT Infrastructure solution. Cloud computing soon be the center of the digital transformation of the IT services industry.


